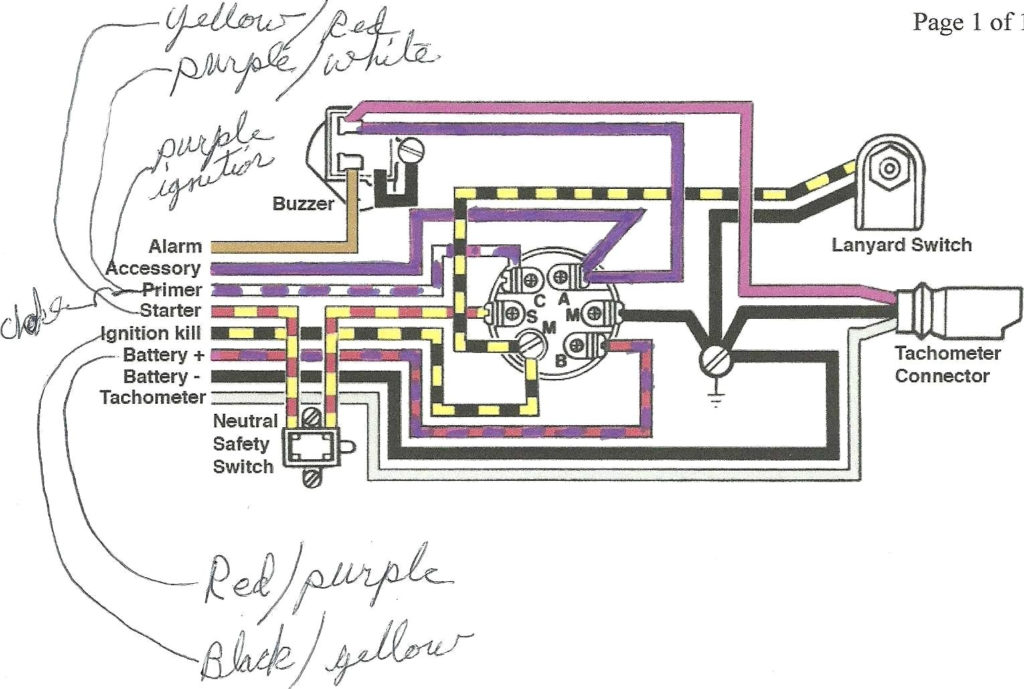
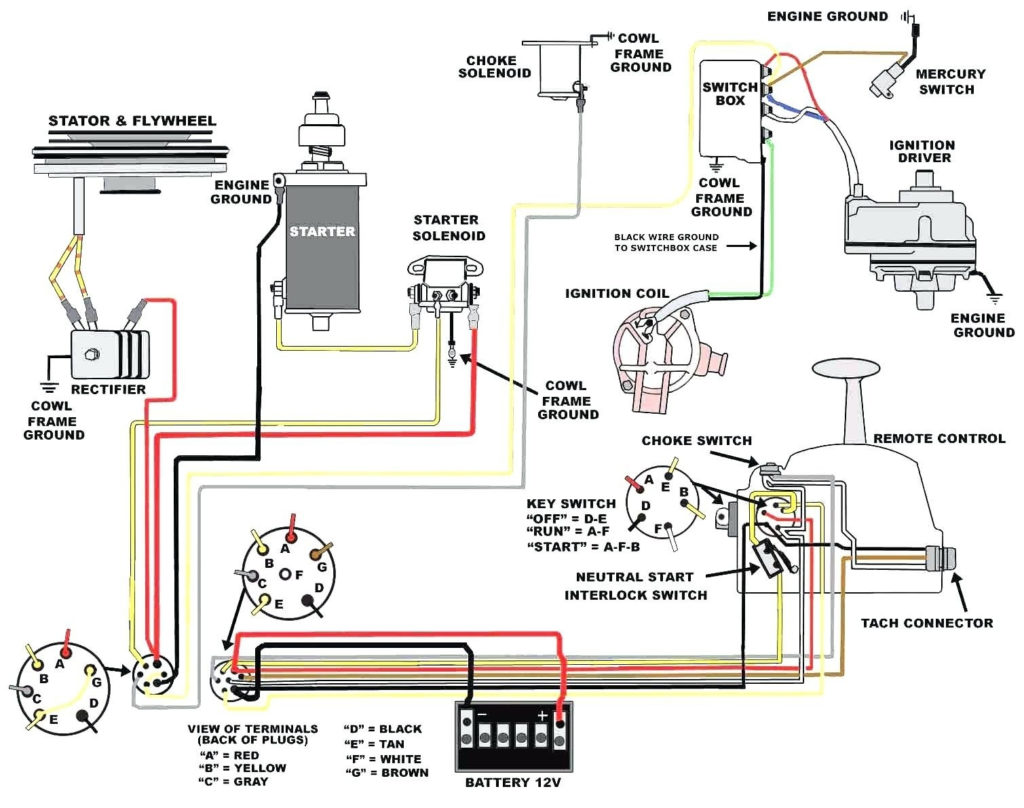
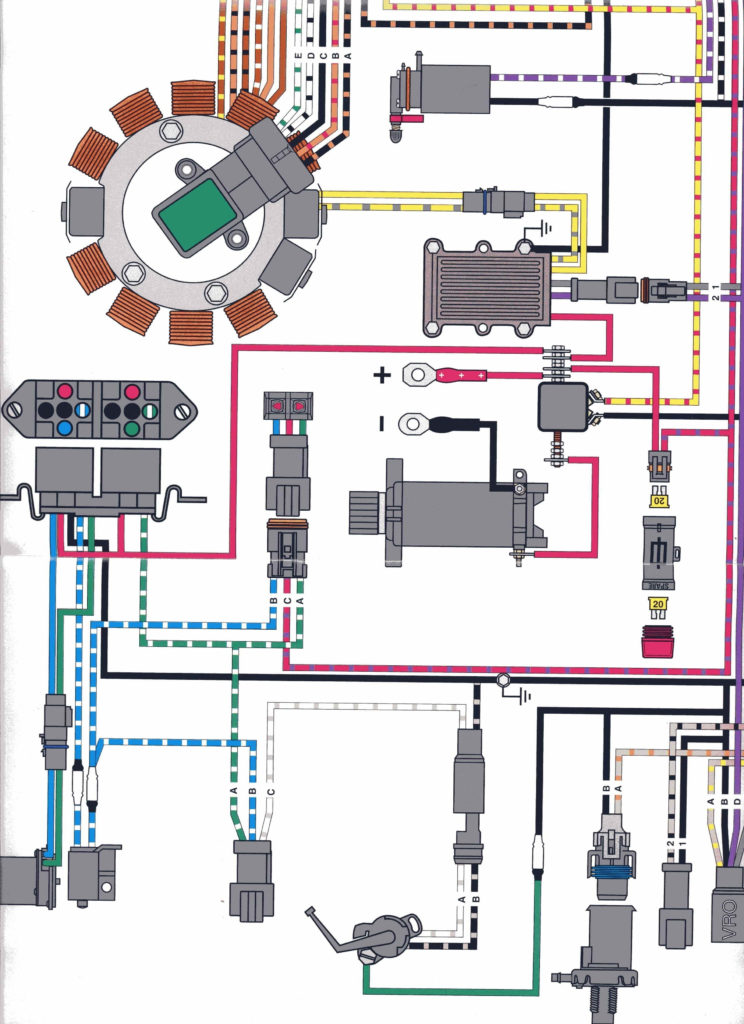
Ignition Key Wiring Diagram – Let’s begin by examining the different kinds and functions of terminals that are found on the ignition switches. These include the terminals that are for the Ignition switch, Coil, and Accessory. Once we know the purpose of these terminals are used for then we can determine the various parts of the Ignition Key Wiring Diagram. We’ll also go over the function of the Ignition switch and Coil. The next step is to focus to the accessory terminals.
Terminals of ignition switch
An ignition switch has three separate switches that feed the battery’s current to various locations. The first switch provides power to the choke while the second toggles the on/off state of the switch. Each manufacturer has its unique color-coding system, which we’ll discuss in a subsequent article. OMC employs this system. The ignition switch comes with a connector for adding the Tachometer.
While most ignition switch terminals can be duplicated, the numbers may not be consistent with the diagram. You should first check the continuity of the wires to determine if they’re connected to the correct ignition switch. This can be done using an inexpensive multimeter. Once you are satisfied with the integrity of the wires, it is time to install the new connector. If your car has an installed ignition switch, the wiring diagram will differ.
It is important to understand the way that ACC outputs and auxiliary outputs function to connect them. The ACC and IGN terminals are the default connections for the ignition switch. the START and IGN terminals are the primary connections to the stereo and radio. The ignition switch turns the engine of your car ON and off. On older vehicles the terminals of the ignition switch are marked with the initials “ACC”, and “ST” (for the individual magnetic wires).
Terminals for coil
The terminology used to determine the type and model of the ignition coil is the most important thing. A basic ignition wiring layout will provide you with a range of terminals and connections. The operating voltage of every coil is different. This is why it is crucial to test the voltage at S1 (primary terminal). S1 should also be tested for resistance to determine if it’s an A, Type B, or A coil.
The negative of the chassis must be connected to the side of low-tension. This is also the ground in the ignition wiring diagram. The high-tension component supplies the spark plugs with positive. The coil’s aluminum body needs to be connected to the chassis to prevent it from being smothered however it’s not electrically required. There are also connections of the negative and positive coil’s terminals on an ignition wiring diagram. Sometimes, a visit to an auto part store can diagnose a malfunctioning ignition wire.
The black-and-white-striped wire from the harness goes to the negative terminal. The terminal that is negative is served by the trace in black that’s joined to the white wire. The black wire connects to the contact breaker. To test the wires’ connections use a paperclip to remove them from the housing. You should also check to ensure that the terminals are not bent.
Accessory terminals
Diagrams of ignition wiring show the various wires that are used for powering the different components. In general there are four distinct colored terminals for each part. To identify accessories, red is for starter solenoid, yellow is for battery and blue for accessories. The “IGN” terminal can be used to start the car and operate the wipers, as well as other operating functions. The diagram illustrates how to connect ACC or ST terminals as well as the rest.
The terminal BAT holds the battery. The electrical system will not start if the battery isn’t connected. Additionally, the switch doesn’t turn on. If you’re not sure of the location of your car’s battery located, you can review the wiring diagram of your car to determine how to locate it. The ignition switch as well as the battery are connected through the accessory terminals. The BAT Terminal is connected to the battery.
Some ignition switches offer an additional “accessory position” that allows users to modify their outputs independent of the ignition. Sometimes, a customer wants to use the auxiliary output separate from the ignition. To make use of the additional output, wire the connector with identical colors to the ignition and connect it to the ACC terminal on the switch. This is a useful option, but there’s one important difference. A majority of ignition switches feature the ACC position when the car is in ACC mode and a START mode when the switch is in IGN.