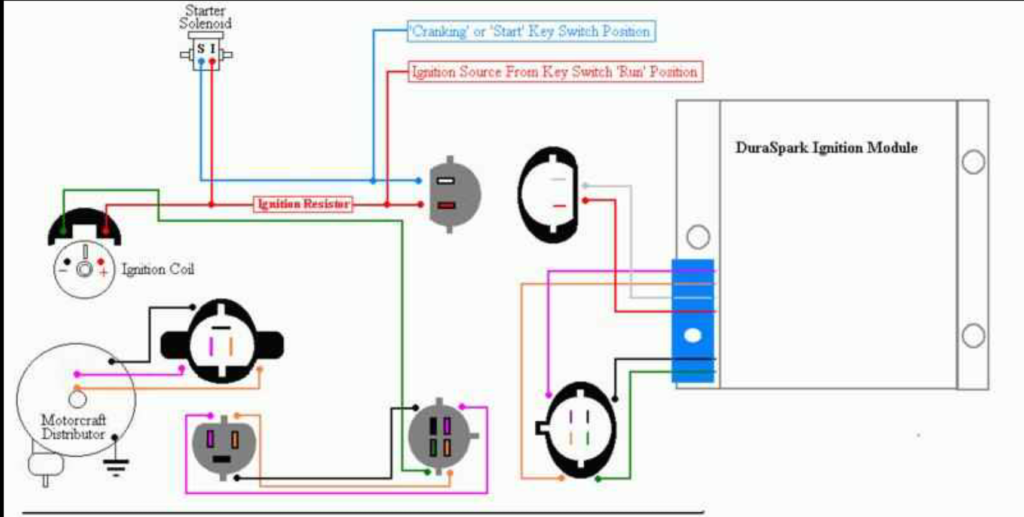
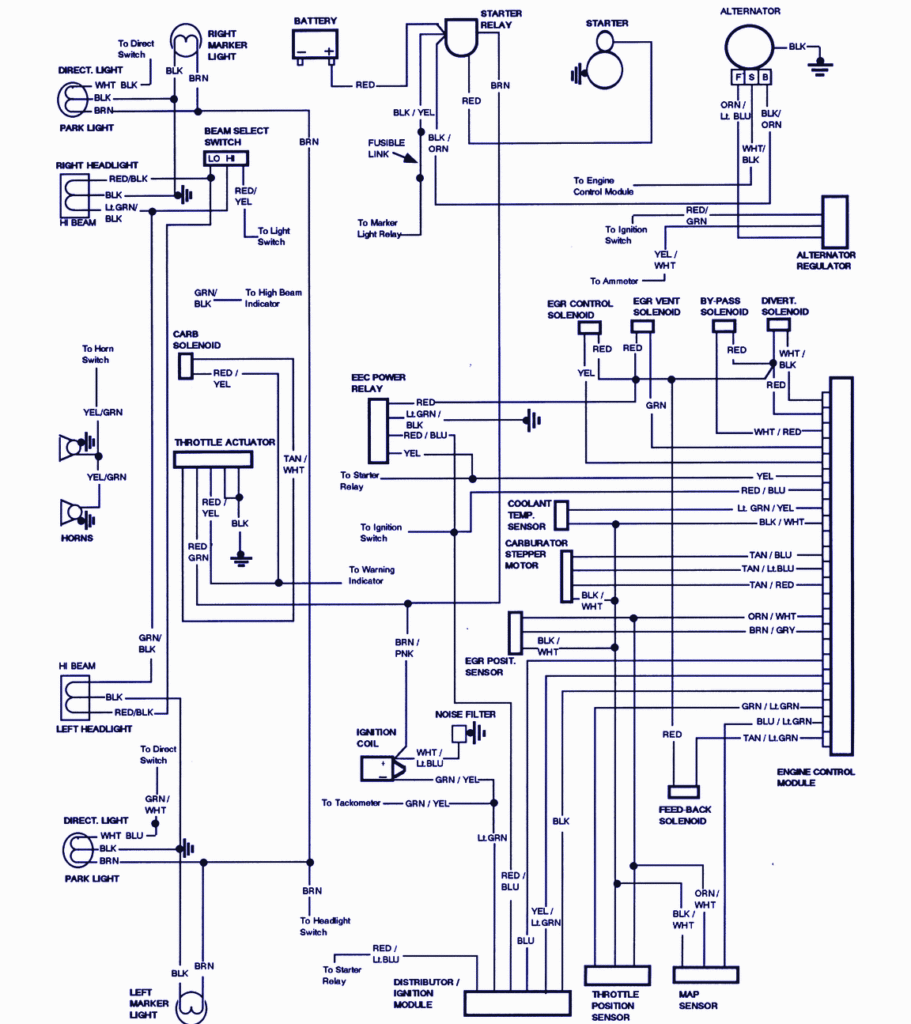
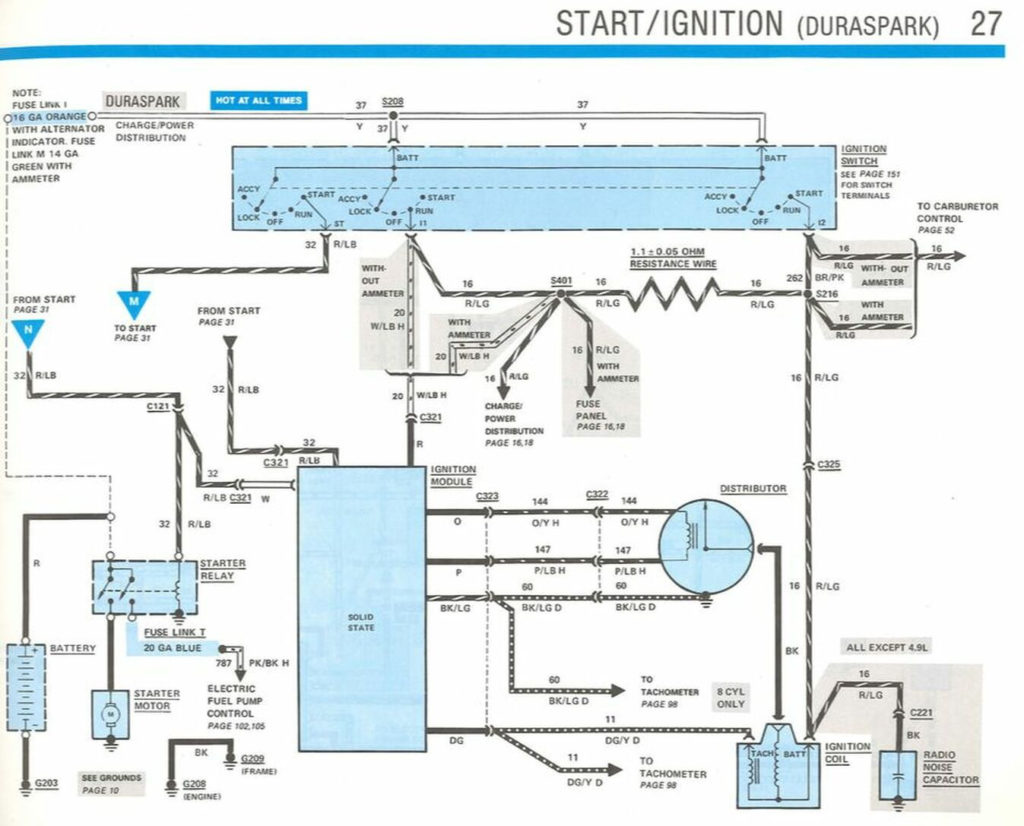
1985 Ford F250 Ignition Wiring Diagram – First, let’s take a look at the different types of terminals on the ignition switch. They include terminals for the Ignition switch, Coil, and Accessory. Once we know the terminals that are utilized, we can begin to identify the different components of the 1985 Ford F250 Ignition Wiring Diagram. We’ll also go over the function of the Ignition switch and Coil. Following that, we will move on to the Accessory Terminals.
The ignition switch’s terminals
An ignition switch has three separate switches that feed the battery’s current to different locations. The ON/OFF position of the ignition switch is controlled by the second switch, which delivers the choke with power when it is pushed. Different manufacturers use different color codes for different conductors. This is discussed in another article. OMC uses the same method. This connector allows the attachment of a speedometer to the ignition switch.
Although the majority of ignition switch terminals may not be original, the numbering for each one may not be in line with the diagram. To make sure that your wires are properly plugged in to the switch it is recommended to check their continuity. A cheap multimeter can aid in this. After you’re satisfied with the integrity of the wires, it is time to install the new connector. The wiring loom used in the ignition system switch supplied by the manufacturer is distinct.
Understanding how the ACC outputs are connected to the other outputs inside your car is vital. The ACC and IGN terminals are the default connections on your ignition switch, and the START and IGN terminals are the principal connections to the stereo and radio. The ignition switch is the engine’s on/off button. The terminals of older cars’ ignition switches are labeled by “ACC” as well as ST (for specific magneto wires).
Terminals for coil
Understanding the terms utilized is the first step in determining what kind of ignition coil to choose. A basic ignition wiring layout will show you a number of connections and terminals. The voltage that operates on each coil differs. This is why it is essential to first check the voltage at the S1 (primary terminal). To determine if the coil is a Type A, C, or B coil, you must also test S1’s resistance.
The low-tension side of the coil must be connected to the chassis’ negative. This is also the ground on an ignition wiring diagram. The high tension part supplies positive power directly to the spark plugs. It is necessary for suppression purposes that the coil’s metallic body be connected to its chassis but not essential. The wiring diagram for the ignition will explain how to connect the two terminals of the positive or negative coils. Sometimes, a malfunctioning ignition coil can be identified through a scan performed at an auto repair shop.
The black-and-white-striped wire from the harness goes to the negative terminal. The white wire also is black with a trace, and it connects to the positive terminal. The black wire goes to the contact breaker. You can take the black wire from the housing of the plug with a paper clip in case you are uncertain about the connection. Make sure that the connectors do not bend.
Accessory terminals
Ignition wiring diagrams show the different wires that are used to power the car’s various parts. There are typically four color-coded terminals that correspond to the respective component. The accessories are red, the battery is yellow and the starter solenoid is green. The “IGN” terminal allows you to start your car, operate the wipers, and any other functions. This diagram shows how you can connect ACC and ST terminals to the rest of components.
The terminal called BAT is the place where the battery is. The battery is vital to allow the electrical system to get started. In addition, the switch will not start. The wiring diagram will tell the location of your car’s battery. The ignition switch is linked to the car’s battery. The BAT terminal is connected to the battery.
Some ignition switches have an “accessory” setting that allows users to regulate their outputs without needing to turn on the ignition. Sometimes, users want to utilize an additional output that is independent of the ignition. To use the additional output, wire the connector in the same colors as ignition and connect it to the ACC terminal on the switch. Although this is a fantastic feature, there’s one thing you should know. Many ignition switches can be configured to be in an ACC position when the vehicle has been moved into the ACC position. They’ll also be in START mode after the vehicle has been moved into the IGN position.